Pegylated IFN-α regulates hepatic gene expression through transient Jak/STAT activation.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
MT Dill, Z Makowska, G Trincucci, AJ Gruber, JE Vogt, M Filipowicz, D Calabrese, I Krol, DT Lau, L Terracciano, E van Nimwegen, V Roth, MH Heim
Pegylated IFN-α regulates hepatic gene expression through transient Jak/STAT activation
The Journal of clinical investigation, 2014, 124 (4), 0-0
Abstract
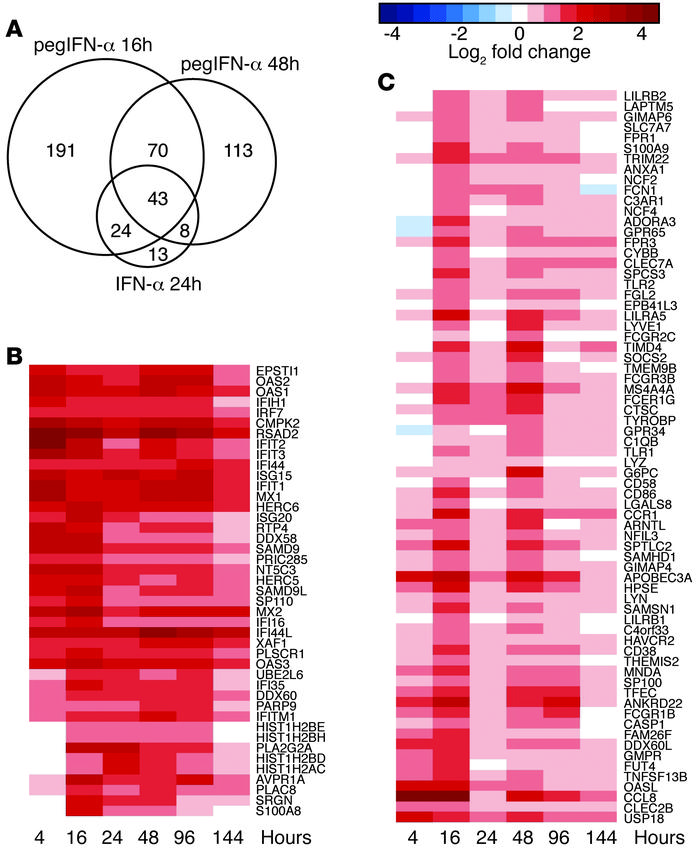
The use of pegylated interferon-α (pegIFN-α) has replaced unmodified recombinant IFN-α for the treatment of chronic viral hepatitis. While the superior antiviral efficacy of pegIFN-α is generally attributed to improved pharmacokinetic properties, the pharmacodynamic effects of pegIFN-α in the liver have not been studied. Here, we analyzed pegIFN-α–induced signaling and gene regulation in paired liver biopsies obtained prior to treatment and during the first week following pegIFN-α injection in 18 patients with chronic hepatitis C. Despite sustained high concentrations of pegIFN-α in serum, the Jak/STAT pathway was activated in hepatocytes only on the first day after pegIFN-α administration. Evaluation of liver biopsies revealed that pegIFN-α induces hundreds of genes that can be classified into four clusters based on different temporal expression profiles. In all clusters, gene transcription was mainly driven by IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3). Compared with conventional IFN-α therapy, pegIFN-α induced a broader spectrum of gene expression, including many genes involved in cellular immunity. IFN-induced secondary transcription factors did not result in additional waves of gene expression. Our data indicate that the superior antiviral efficacy of pegIFN-α is not the result of prolonged Jak/STAT pathway activation in hepatocytes, but rather is due to induction of additional genes that are involved in cellular immune responses.
Short URL: https://tinyurl.com/y3pppkmh





Comments and Reactions
No comments yet. Why don't you write one?