published
Monitoring single-cell gene regulation under dynamically controllable conditions with integrated microfluidics and software
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
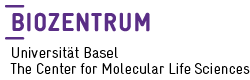
Erik van Nimwegen Monitoring single-cell gene regulation under dynamically controllable conditions with integrated microfluidics and software, BioRxiv 2016, doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02505-0 Abstract Much is still not understood about how gene regulatory interactions control cell fate decisions in single cells, in part due to the difficulty of directly observing gene regulatory processes in vivo. We introduce here a novel integrated setup consisting of a microfluidic chip and accompanying analysis software that enable long-term quantitative tracking of growth and gene expression in single cells. The dual-input Mother Machine (DIMM) chip enables controlled and continuous variation of external conditions, allowing direct observation of gene regulatory responses to changing conditions in single cells. The Mother Machine Analyzer (MoMA) software achieves unprecedented accuracy in segmenting and tracking cells, and streamlines high-throughput curation with a novel leveraged editing procedure. We demonstrate the power of the method by uncovering several novel features of an iconic gene regulatory program: Read the full story »
Read moreAutomated incorporation of pairwise dependency in transcription factor binding site prediction using dinucleotide weight tensors
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
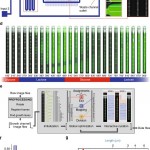
Saeed Omidi, Mihaela Zavolan, Mikhail Pachkov, Jeremie Breda, Severin Berger, Erik van Nimwegen Automated incorporation of pairwise dependency in transcription factor binding site prediction using dinucleotide weight tensors, PLoS Computational Biology 2017, doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005176 Abstract Gene regulatory networks are ultimately encoded by the sequence-specific binding of (TFs) to short DNA segments. Although it is customary to represent the binding specificity of a TF by a position-specific weight matrix (PSWM), which assumes each position within a site contributes independently to the overall binding affinity, evidence has been accumulating that there can be significant dependencies between positions. Unfortunately, methodological challenges have so far hindered the development of a practical and generally-accepted extension of the PSWM model. On the one hand, simple models that only consider dependencies between nearest-neighbor positions are easy to use in practice, but fail to account for the distal dependencies that are observed in the data. On the other hand, Read the full story »
Read moreThe genomic context and corecruitment of SP1 affect ERRα coactivation by PGC-1α in muscle cells
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
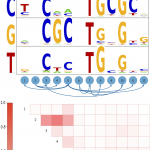
Silvia Salatino, Barbara Kupr, Mario Baresic, Erik van Nimwegen, Christoph Handschin The Genomic Context and Corecruitment of SP1 Affect ERRα Coactivation by PGC-1α in Muscle Cells, Molecular Endocrinology 30:7;809-825,2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2016-1036 Abstract The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) coordinates the transcriptional network response to promote an improved endurance capacity in skeletal muscle, eg, by coactivating the estrogen-related receptor-α (ERRα) in the regulation of oxidative substrate metabolism. Despite a close functional relationship, the interaction between these 2 proteins has not been studied on a genomic level. We now mapped the genome-wide binding of ERRα to DNA in a skeletal muscle cell line with elevated PGC-1α and linked the DNA recruitment to global PGC-1α target gene regulation. We found that, surprisingly, ERRα coactivation by PGC-1α is only observed in the minority of all PGC-1α recruitment sites. Nevertheless, a majority of PGC-1α target gene expression is dependent on ERRα. Intriguingly, the interaction Read the full story »
Read moreARMADA: Using motif activity dynamics to infer gene regulatory networks from gene expression data
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment

PJ Pemberton-Ross, M Pachkov, E van Nimwegen
ARMADA: Using motif activity dynamics to infer gene regulatory networks from gene expression data, Methods 2015 85:62-74,
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.06.024
Expression noise facilitates the evolution of gene regulation
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment

Luise Wolf, Olin K Silander, Erik van Nimwegen
Expression noise facilitates the evolution of gene regulation, eLife 2015;4:e05856,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05856.001
Jeremie Breda, Andrzej J Rzepiela, Rafal Gumienny, Erik van Nimwegen, Mihaela Zavolan
Quantifying the strength of miRNA–target interactions, Methods 2015 85:90-99,
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.04.012
A large-scale, in vivo transcription factor screen defines bivalent chromatin as a key property of regulatory factors mediating Drosophila wing development
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment

C Schertel, M Albarca, C Rockel-Bauer, NW Kelley, J Bischof, K Hens, E van Nimwegen, K Basler, B Deplancke
A large-scale, in vivo transcription factor screen defines bivalent chromatin as a key property of regulatory factors mediating Drosophila wing development, Genome research2015 25: 514-523,
doi: 10.1101/gr.181305.114
Download pdf
Supplemental Material
Global 3′ UTR shortening has a limited effect on protein abundance in proliferating T cells
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
AR Gruber, G Martin, P Müller, A Schmidt, AJ Gruber, R Gumienny, N Mittal, R Jayachandran, J Pieters, W Keller, E van Nimwegen, M Zavolan
Global 3′ UTR shortening has a limited effect on protein abundance in proliferating T cells,Nature Communications 2014 5:5465,
doi:10.1038/ncomms6465
Optimal joint segmentation and tracking of Escherichia coli in the mother machine
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
F Jug, T Pietzsch, D Kainmüller, J Funke, M Kaiser, E van Nimwegen, C Rother, G Myers
Optimal joint segmentation and tracking of Escherichia coli in the mother machine, Bayesian and grAphical Models for Biomedical Imaging. Lecture Notes in Computer Science Volume 8677, 2014, pp 25-36,
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12289-2_3
Transcriptional network analysis in muscle reveals AP-1 as a partner of PGC-1α in the regulation of the hypoxic gene program.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
M Baresic, S Salatino, B Kupr, E van Nimwegen, C Handschin
Transcriptional network analysis in muscle reveals AP-1 as a partner of PGC-1α in the regulation of the hypoxic gene program
Molecular and cellular biology, 2014, MCB. 01710-13
Download pdf
Supplemental material