Transcriptional network analysis in muscle reveals AP-1 as a partner of PGC-1α in the regulation of the hypoxic gene program.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
M Baresic, S Salatino, B Kupr, E van Nimwegen, C Handschin
Transcriptional network analysis in muscle reveals AP-1 as a partner of PGC-1α in the regulation of the hypoxic gene program
Molecular and cellular biology, 2014, MCB. 01710-13
ABSTRACT
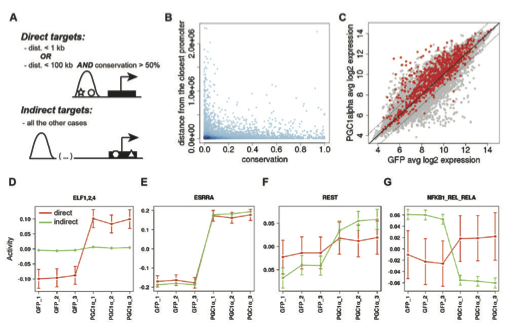
Skeletal muscle tissue shows an extraordinary cellular plasticity, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are still poorly understood. Here we use a combination of experimental and computational approaches to unravel the complex transcriptional network of muscle cell plasticity centered on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), a regulatory nexus in endurance training adaptation. By integrating data on genome-wide binding of PGC-1α and gene expression upon PGC-1α over-expression with comprehensive computational prediction of transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs), we uncover a hitherto underestimated number of transcription factor partners involved in mediating PGC-1α action. In particular, principal component analysis of TFBSs at PGC-1α binding regions predicts that, besides the well-known role of the estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα), the activator protein-1 complex (AP-1) plays a major role in regulating the PGC-1α-controlled gene program of hypoxia response. Our findings thus reveal the complex transcriptional network of muscle cell plasticity controlled by PGC-1α.
Download pdf
Supplemental material
Short URL: https://tinyurl.com/yyxgedja





Comments and Reactions
No comments yet. Why don't you write one?