Publications
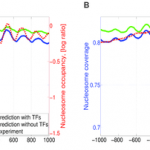
Nucleosome free regions in yeast promoters result from competitive binding of transcription factors that interact with chromatin modifiers/
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
EA Ozonov and E van Nimwegen
Nucleosome free regions in yeast promoters result from competitive binding of transcription factors that interact with chromatin modifiers
PLoS computational biology, 2013, 9 (8), e1003181
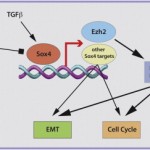
Sox4 is a master regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by controlling Ezh2 expression and epigenetic reprogramming.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
N Tiwari, VK Tiwari, L Waldmeier, PJ Balwierz, P Arnold, M Pachkov, N Meyer-Schaller, D Schübeler, E van Nimwegen and G Christofori
Sox4 is a master regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by controlling Ezh2 expression and epigenetic reprogramming
Cancer Cell, 2013 23 (6), 768-783
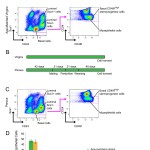
Parity induces differentiation and reduces Wnt/Notch signaling ratio and proliferation potential of basal stem/progenitor cells isolated from mouse mammary epithelium
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
F Meier-Abt, E Milani, T Roloff, H Brinkhaus, S Duss, DS Meyer, I Klebba, PJ Balwierz, E Van Nimwegen and M Bentires-Alj
Parity induces differentiation and reduces Wnt/Notch signaling ratio and proliferation potential of basal stem/progenitor cells isolated from mouse mammary epithelium
Breast Cancer Research, 2013, 15 (2), R36
Download pdf
Supplemental material
Klf4 is a transcriptional regulator of genes critical for EMT, including Jnk1 (Mapk8).
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
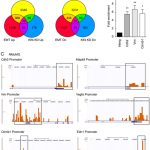
N Tiwari, N Meyer-Schaller, P Arnold, H Antoniadis, M Pachkov, E van Nimwegen, G Christofori
Klf4 is a transcriptional regulator of genes critical for EMT, including Jnk1 (Mapk8)
PloS one, 2013, 8 (2), e57329
Quantitative analysis of persister fractions suggests different mechanisms of formation among environmental isolates of E. coli.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
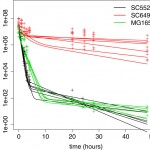
N Hofsteenge, E van Nimwegen, OK Silander
Quantitative analysis of persister fractions suggests different mechanisms of formation among environmental isolates of E. coli
BMC microbiology, 2013, 13 (1), 25
Download pdf
Supplemental material
A biophysical miRNA-mRNA interaction model infers canonical and noncanonical targets.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
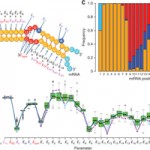
M Khorshid, J Hausser, M Zavolan and E van Nimwegen
A biophysical miRNA-mRNA interaction model infers canonical and noncanonical targets
Nature methods, 2013, 10 (3), 253-255
Rahul Siddharthan, Erik van Nimwegen Detecting regulatory sites using PhyloGibbs. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.),2007, 395, 381-402.
Read moreFinding regulatory elements and regulatory motifs: a general probabilistic framework.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
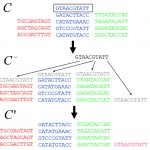
E. van Nimwegen Finding regulatory elements and regulatory motifs: a general probabilistic framework. BMC Bioinformatics, 2007, 8 Suppl 6, S4.
Read moreInference of miRNA targets using evolutionary conservation and pathway analysis.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment
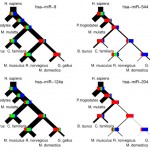
D. Gaidatzis, E. van Nimwegen, J. Hausser, M. Zavolan Inference of miRNA targets using evolutionary conservation and pathway analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 2007, 8, 69
Read moreSwissRegulon: a database of genome-wide annotations of regulatory sites.
Posted in Publications, publishedNo Comment

M. Pachkov, I. Erb, N. Molina, E. van Nimwegen SwissRegulon: a database of genome-wide annotations of regulatory sites. Nucleic Acids Research, 35(Database issue), 2007, D127-31.
Read more